CUDA Kernel Launch Statistics
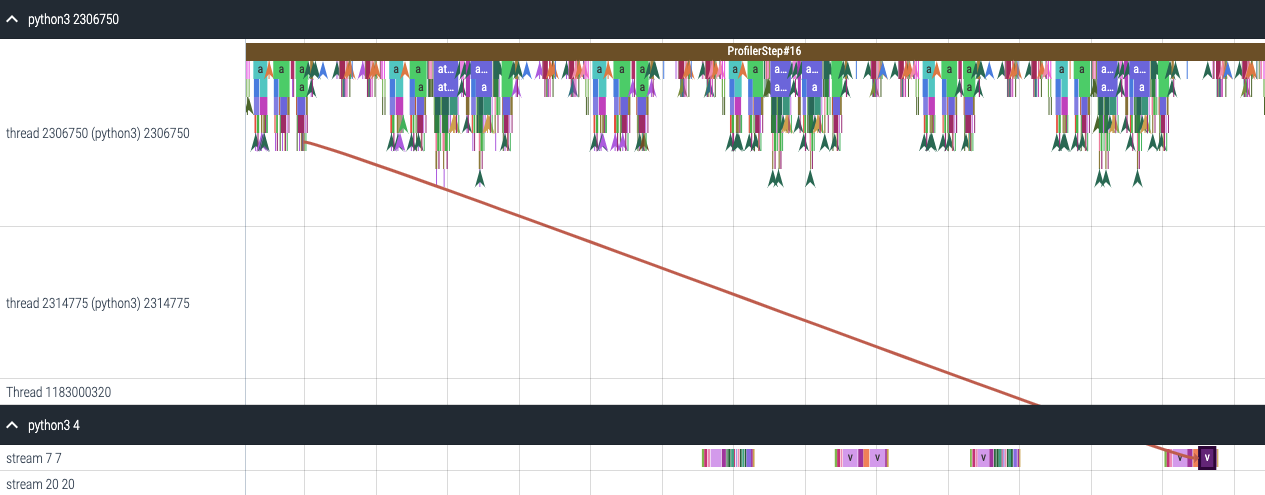
For each event launched on the GPU there is a corresponding scheduling event on the CPU e.g. CudaLaunchKernel, CudaMemcpyAsync, CudaMemsetAsync. These events are linked by a common correlation id in the trace. See figure above. This feature computes the duration of the CPU runtime event, its corresponding GPU kernel and the launch delay i.e. the difference between GPU kernel starting and CPU operator ending. The kernel launch info can be generated as follows:
analyzer = TraceAnalysis(trace_dir="/path/to/trace/dir")
kernel_info_df = analyzer.get_cuda_kernel_launch_stats()
A screenshot of the generated dataframe is given below.
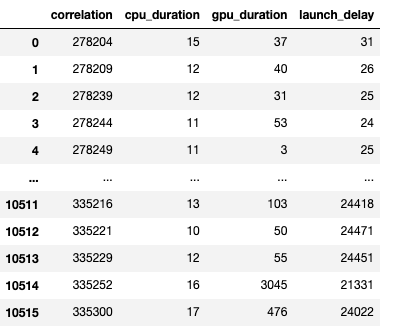
The duration of the CPU op, GPU kernel and the launch delay allows us to find:
Short GPU kernels - GPU kernels with duration less than the corresponding CPU runtime event.
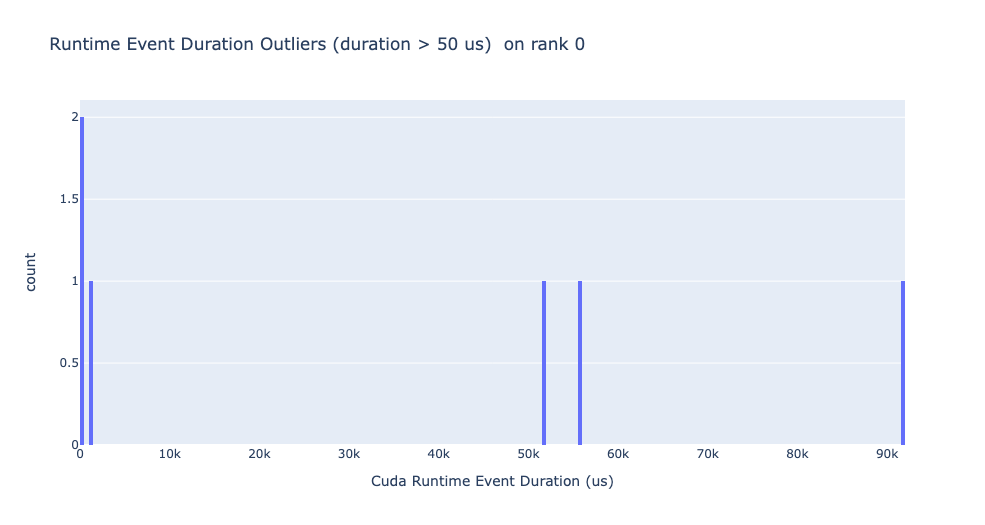
Runtime event outliers - CPU runtime events with excessive duration.
Launch delay outliers - GPU kernels which take too long to be scheduled.
HTA generates distribution plots for each of the aforementioned three categories.
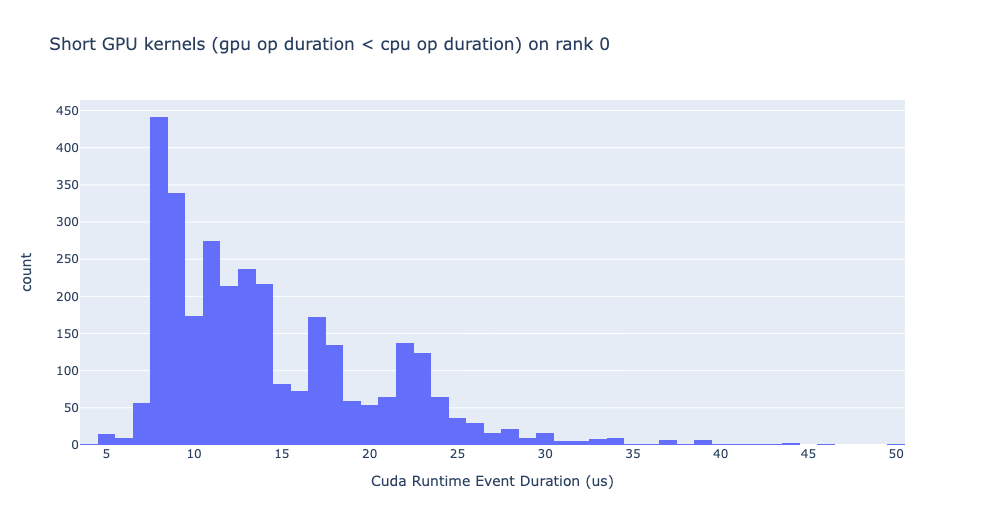
Short GPU kernels
Usually, the launch time on the CPU side is between 5-20 microseconds. In some cases the GPU execution time is lower than the launch time itself. The graph below allows us to find how frequently such instances appear in the code.
Runtime event outliers
The runtime outliers depend on the cutoff used to classify the outliers, hence
the get_cuda_kernel_launch_stats
API provides the runtime_cutoff argument to configure the value.
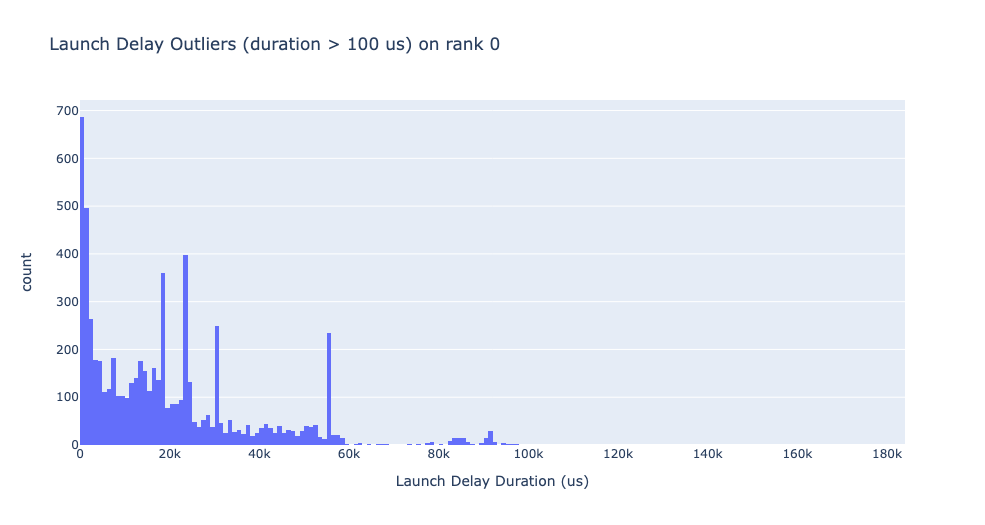
Launch delay outliers
The launch delay outliers depend on the cutoff used to classify the outliers,
hence the get_cuda_kernel_launch_stats
API provides the launch_delay_cutoff argument to configure the value.